Auth0 JWT Integration with Hasura GraphQL engine
Introduction
This page helps you to set up Auth0 to work with the Hasura GraphQL engine.
Create an Auth0 Application
- Navigate to the Auth0 dashboard.
- Click on the
Applicationsmenu option on the left, then click the+ Create Applicationbutton. - In the
Create Applicationwindow, set a name for your application, and selectSingle Page Web Applications. (assuming your application is React/Angular/Vue etc).

You get the basic information such as the Domain, Client ID, and Client Secret from the Applications > Settings
tab once the application is created.
Configure Auth0 Rules & Callback URLs
In the Applications > Settings > Application URIs section, set Allowed Callback URLs to http://jwt.io. Select
Save Changes.
Add domain-specific URLs as well for the production apps (e.g: https://myapp.com/callback).
Disable the OIDC Conformant under Applications > Settings > Advanced Settings > OAuth section to avoid callback
error.
Auth0 has multiple versions of its SDK that use different semantics to handle JWT.
- If you're using Auth0.js, add a rule to update the
idToken. - If you're using the Auth0 Single Page App SDK, add a rule to update
the
accessToken.
Your client will not authenticate your app if a wrong token gets updated, as the necessary Hasura claims won't appear in the generated JWT.
In both cases, navigate to Auth Pipeline > Rules and create a rule here to add the custom JWT claims. You can choose
any name for the rule.
For Auth0.js:
function (user, context, callback) {
const namespace = "https://hasura.io/jwt/claims";
context.idToken[namespace] =
{
'x-hasura-default-role': 'user',
// do some custom logic to decide allowed roles
'x-hasura-allowed-roles': ['user'],
'x-hasura-user-id': user.user_id
};
callback(null, user, context);
}
For auth0-spa-js:
function (user, context, callback) {
const namespace = "https://hasura.io/jwt/claims";
context.accessToken[namespace] =
{
'x-hasura-default-role': 'user',
// do some custom logic to decide allowed roles
'x-hasura-allowed-roles': ['user'],
'x-hasura-user-id': user.user_id
};
callback(null, user, context);
}
Create an Auth0 API
For auth0-spa-js, also create an API so that the access token issued by Auth0 follows the JWT standard. Read more
about this here.
Navigate to Auth0 dashboard. Click on the APIs menu option on the left sidebar and click
the + Create API button.
In the New API window, set a name for your API and enter an identifier (e.g. hasura). In your application code,
configure your API identifier as the audience when initializing Auth0.
For example:
<Auth0Provider
domain={process.env.AUTH_DOMAIN}
client_id={process.env.AUTH_CLIENT_ID}
redirect_uri={window.location.origin}
onRedirectCallback={() => ..}
audience="hasura"
>
Test auth0 login and generate sample JWTs for testing
You don't need to integrate your UI with Auth0 for testing. There are 2 ways you can test connections:
If you are logged in to the Auth0 Dashboard:
Navigate to Auth0 Dashboard, and select
Authentication. Select the type of connection you want to test and selectTry Connection.If you are not logged in to the Auth0 Dashboard:
Use the Test partner connections embed link. Select
LOG INto login to your Auth0 domain.Select your application and copy the generated URL, like so:
https://dev-m-lbqrnq.us.auth0.com/authorize?response_type=token&scope=openid%20profile&client_id=BDAXJbE7Hw0Jhm4CL0UlAXmgrwebDFfj&redirect_uri=http://jwt.io&connection=THE_CONNECTION_YOU_WANT_TO_TEST
client_id: Client ID of the application. This value is auto-filled from your application.connection: Name of the connection you want to test.Applications > <application_name> > Connections
For example, to test the connection for
Username-Password-Authentication, modify the above URL as:https://dev-m-lbqrnq.us.auth0.com/authorize?response_type=token&scope=openid%20profile&client_id=DCcIkeWPNxtDEjdiI94SODLQEB2WBuYb&redirect_uri=http://jwt.io&connection=Username-Password-AuthenticationOnce you follow the link, you will be redirected to your configured identity provider. After successful login, you will be sent back to JWT.io to decode, verify and generate JWT.

Save this JWT token value to be used later to test authorization using the Hasura console.
Configure Hasura to use Auth0 Keys
Auth0 publishes their JWK under:
https://<your-auth0-domain>.auth0.com/.well-known/jwks.json
But they have a bug where the certificate thumbprint does not match. Hence, this URL does not work with Hasura.
The current workaround is to download the X590 certificate from:
https://<your-auth0-domain>.auth0.com/pem and use it in the key field:
{
"type":"RS512",
"key": "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIDDTCAfWgAwIBAgIJhNlZ11IDrxbMA0GCSqSIb3DQEBCwUAMCQxIjAgBgNV
BAMTGXlc3QtaGdlLWp3C5ldS5hdXRoMC5jb20HhcNMTgwNzMwMTM1MjM1WhcN
MzIwND3MTM1MjM1WjAkSIwIAYDVQQDExl0ZXNLWhnZS1qd3QuZXUuYXV0aDAu
Y29tMIBIjANBgkqhkiGw0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIICgKCAQEA13CivdSkNzRnOnR5
ZNiReD+AgbL7BWjRiw3RwjxRp5PYzvAGuj94yR6LRh3QybYtsMFbSg5J7fNq6
Ld6yMpMrUu8CBOnYY456b/2jlf+Vp8vEQuKvPOOw8Ev6x7X3blcuXCELSwyL3
AGHq9OP2RV6V6CIE863zzuYH5HDLzU35oMZqogJVRJM0+6besH6TnSTNiA7xi
BAqFaiRNQRVi1CAUa0bkN1XRp4AFy7d63VldOsM+8QnCNHySdDr1XevVuq6DK
LQyGexFy4niALgHV0Q7A+xP1c2G6rJomZmn4j1avnlBpU87E58JMrRHOCj+5m
Xj22/QDAQABo0IwQDAPgNVHRMBAf8EBTADAQHMB0GA1UdDgQWBBT6FvNkuUgu
tk3OYQi4lo5aOgwazAOgNVHQ8BAf8EBAMCAoQDQYJKoZIhvcNAQELBQADggEB
ADCLj+L22pEKyqaIUlhUJh7DAiDSLafy0fw56CntzPhqiZVVRlhxeAKidkCLV
r9IEbRuxUoXiQSezPqM//9xHegMp0f2VauVCFg7EpUanYwvqFqjy9LWgH+SBz
4uroLSZ5g1EPsHtlArLChA90caTX4e7Z7Xlu8G2kHRJB5nC7ycdbMUvEWBMeI
tn/pcbmZ3/vlgj4UTEnURe2UPmSJpxmPwXqBcvwdKHRMgFXhZxojWCi0z4ftf
f8t8UJIcbEblnkYe7wzYy8tOXoMMHqGSisCdkp/866029rJsKbwd8rVIyKNC5
frGYaw+0cxO6/WvSir0eA=
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
"
}
An easier way to generate the above config is to use the following UI: https://hasura.io/jwt-config/.
You can use the generated config in the HASURA_GRAPHQL_JWT_SECRET env variable or --jwt-secret flag.
You can directly copy-paste the config in yaml files and command-line arguments as it takes care of escaping the new
lines.

Add Access Control Rules via Hasura Console
Auth0 is configured and ready to be used in the application. You can now set up access control rules that are automatically applied whenever a client makes a GraphQL request with the Auth0 token.
Refer to Access control basics for more information.
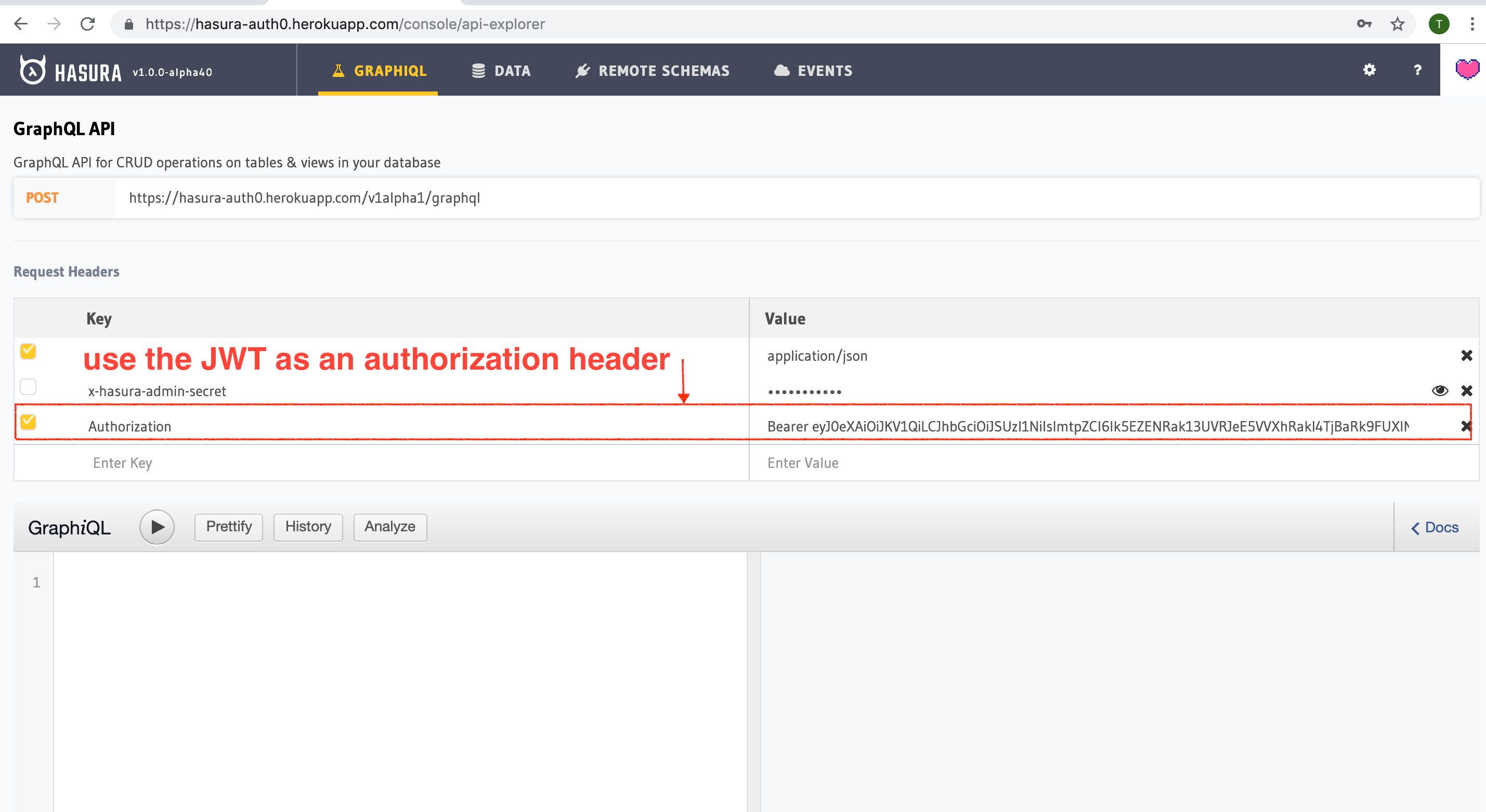
Add an access control rule that uses x-hasura-user-id for the role user. Then make a GraphQL query or a mutation,
with the authorization token from the previous step where we generated an Auth0 token.
You can also use the env variable HASURA_GRAPHQL_UNAUTHORIZED_ROLE or --unauthorized-role flag to set a role for
unauthorized users (e.g. anonymous). This allows you to set permissions for users that are not logged in.
The configured unauthorized role is used whenever an access token is not present in a request to the GraphQL API.
This is useful for data that you would like anyone to be able to access and can be configured and restricted just like any other role.
Sync Users from Auth0
Now that you have created an Auth0 application and can sign up/login, you will need a way to sync your users in Postgres
as well. All you need is the Auth0 user_id in something like a users table.
Using Auth0 Rules again, add the following rule which will insert a new user every time someone signs up.
function (user, context, callback) {
const userId = user.user_id;
const url = "https://my-hasura-app.hasura.app/v1/graphql";
const upsertUserQuery = `
mutation($userId: String!){
insert_users(objects: [{ id: $userId }], on_conflict: { constraint: users_pkey, update_columns: [] }) {
affected_rows
}
}`
const graphqlReq = { "query": upsertUserQuery, "variables": { "userId": userId } }
request.post({
headers: {'content-type' : 'application/json', 'x-hasura-admin-secret': configuration.HASURA_ADMIN_SECRET},
url: url,
body: JSON.stringify(graphqlReq)
}, function(error, response, body){
console.log(body);
callback(null, user, context);
});
}
Make sure to specify the HASURA_ADMIN_SECRET variable in the Rules > Settings section of Auth0.
That’s it! This rule will be triggered on every successful sign up/login and sync your Auth0 user into your postgres database.
We need to use an upsert operation here because social logins do not distinguish between sign-up and login. Hence, we
need to run this rule every time a successful login is made and do nothing if the user already exists.
The sync step will require a reachable endpoint to Hasura and this is not possible in localhost. You can use ngrok or similar services to expose your locally running Hasura with a public endpoint temporarily.
Incorporate Auth0 with a full-stack application - Learn Tutorials.

